Published Projects
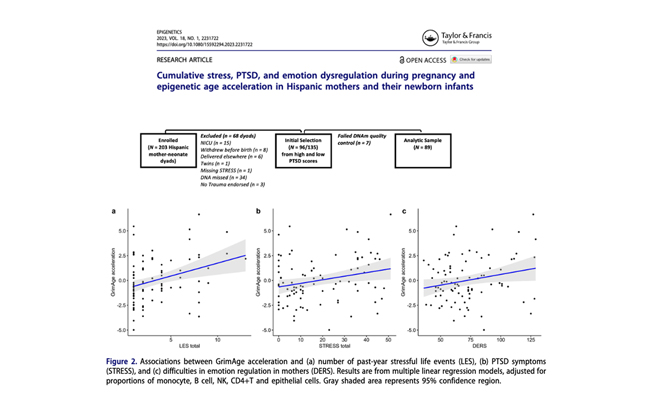
Cumulative stress, PTSD, and emotion dysregulation during pregnancy and epigenetic age acceleration in Hispanic mothers and their newborn infants
Journal: Epigenetics (Accepted), 2023
Here, we evaluated the associations between PTSD symptoms, maternal DNA methylation (DNAm) GrimAge acceleration, which is an epigenetic predictor of mortality, and gestational epigenetic age acceleration in 89 maternal-neonatal dyads
Platform: Infinium MethylationEPIC BeadChip
Tools used: R, bioconductor
Check it out on PubMed Github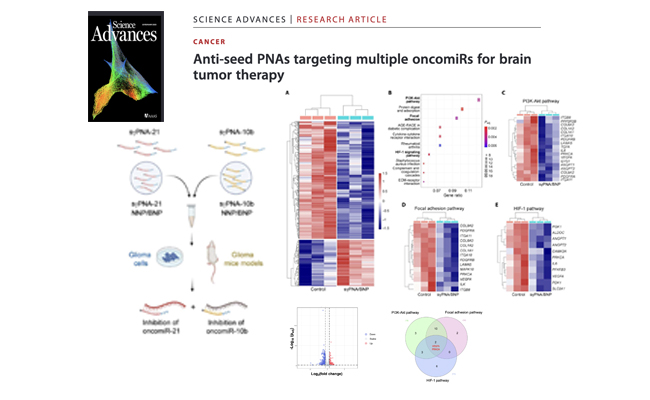
Anti-seed PNAs targeting multiple oncomiRs for brain tumor therapy.
Journal: Science Advances 2023 Feb 10;9(6)
Glioblastoma (GBM) is one of the most lethal malignancies with poor survival and high recurrence rates. Here, we aimed to simultaneously target oncomiRs 10b and 21, reported to drive GBM progression and invasiveness.
Tools used: Fastqc, Trimmomatic, HiSAT2, HTSeq-count, R, DESeq2, Database querying (TCGA)
Check it out on PubMed Github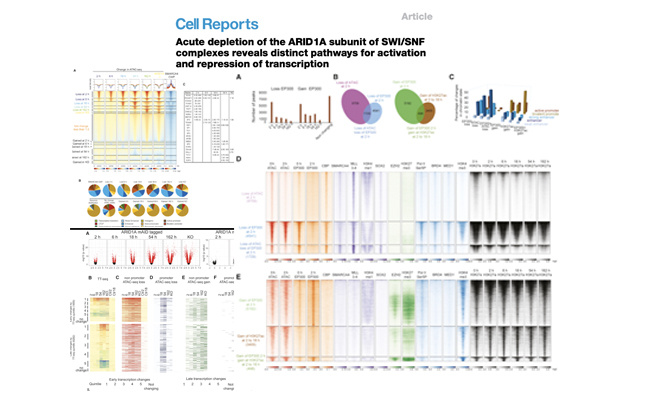
Acute depletion of the ARID1A subunit of SWI/SNF complexes reveals distinct pathways for activation and repression of transcription">Article TITLE
Journal: Cell Rep. 2021 Nov 2;37(5)
The ARID1A subunit of SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complexes is a potent tumor suppressor. Here, a degron is applied to detect rapid loss of chromatin accessibility at thousands of loci where ARID1A acts to generate accessible minidomains of nucleosomes.
Tools used:Python, R, Linux, Fastqc, Trimmomatic, HiSAT2, HTSeq-count, MACS2, DiffBind, Bedtools, EdgeR, Deeptools
Check it out on PubMed Github
Complete mitochondrial genome of the Caribbean reef shark, Carcharhinus perezi (Carcharhinformes: Carcharhinidae).
Authors: Gallagher AJ, Shipley ON, Reese B, Singh V.
Journal: Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2021 Aug 19;6(9):2662-2664.
We report the mitogenome sequence of the Caribbean reef shark to be 16,709 bp and composed two rRNA genes, 22 tRNA genes, 13 protein-coding genes, 2 non-coding regions; the D-loop control region and the origin of light-strand replication. We build bayesian inference tree of the phylogenetic relationships among 16 shark species within the Order Carcharhiniformes.
Tools used: Fastqc, Trimmomatic, MitoZ, MUSCLE, GetOrganelle
Check it out on PubMed Github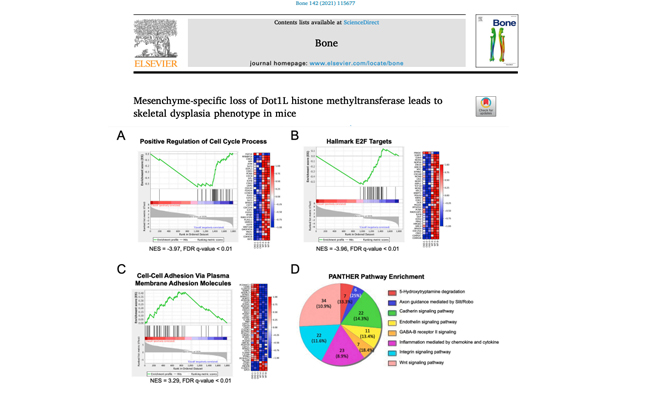
Mesenchyme-specific loss of Dot1L histone methyltransferase leads to skeletal dysplasia phenotype in mice.
Journal: Bone 2021 Jan; 142:115677.
We report a novel skeletal dysplasia phenotype in mice with conditional loss of Disruptor of telomeric silencing 1-like (Dot1L) histone methyltransferase in limb mesenchymal progenitors and downstream descendants. RNAseq analysis of Dot1L deficient chondrocytes implicated Dot1L in the regulation of key genes and pathways necessary to promote cell cycle regulation and skeletal growth.
Tools used: Fastqc, Trimmomatic, HiSAT2, HTSeq-count, R, DESeq2, GSEA, IPA, Panther
Check it out on PubMed Github
High gene space divergence contrasts with frozen vegetative architecture in the moss family Funariaceae.
Authors: Rahmatpour N, Perera NV, Singh V., Wegrzyn JL, Goffinet B.
Journal: Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2021 Jan;154
We analyzed the vegetative gametophytic transcriptome of F. hygrometrica and P. pyriforme and mapped short reads, transcripts, and proteins to the genome and gene space of P. patens.
Tools used: Fastqc, Trimmomatic, Bowtie2, Kallisto, R, Trinity, Transdecoder, EnTAP, BUSCO, RNAQuast, VSEARCH, hmmSCAN
Check it out on PubMed Github
The Potential Role of Preoperative Pain, Catastrophizing, and Differential Gene Expression on Pain Outcomes after Pediatric Spinal Fusion.
Authors: Perry M, Sieberg CB, Young EE, Baumbauer K, Singh V, Wong C, Starkweather A.
Journal: Pain Manag Nurs. 2021 Feb;22(1):44-49.
While adolescent idiopathic scoliosis is not often classified as a painful condition, providers must be cognizant of pre-existing pain and anxiety that may precipitate a negative recovery trajectory. Policy and practice change are essential for early identification and subsequent intervention.
Tools used: Fastqc, Trimmomatic, HiSAT2, HTSeq-count, R, DESeq2, GSEA
Check it out on PubMed Github
Nuclear receptor Ftz-f1 promotes follicle maturation and ovulation partly via bHLH/PAS transcription factor Sim.
Authors: Knapp EM., Li W., Singh V., Sun J.
Journal: eLife 2020; 9: e54568
Here, we discover that Ftz-f1, one of the NR5A nuclear receptors in Drosophila, is transiently induced in follicle cells in late stages of oogenesis via ecdysteroid signaling. Genetic disruption of Ftz-f1 expression prevents follicle cell differentiation into the final maturation stage, which leads to anovulation.
Tools used: Fastqc, Trimmomatic, HiSAT2, HTSeq-count, R, DESeq2, CUT&RUN, MACS2, MEME2, Bowtie2
Check it out on PubMed Github
Investigating global gene expression changes in a murine model of cherubism.
Authors: Sharma T, Cotney J, Singh V, Sanjay A., Reichenberger EJ., Ueki Y.,
Journal: Bone. 2020; 135:115315.
To develop a deeper understanding for the potential underlying mechanisms for Cherubism, a rare genetic disorder, we compared global gene expression changes in hematopoietic and mesenchymal cell populations between cherubism and wild type mice.These studies reveal complex changes in gene expression elicited from a cherubic mutation in Sh3bp2 that are informative to the mechanisms responding to inflammatory stimuli and repressing osteogenesis.
Tools used: Fastqc, Trimmomatic, HiSAT2, HTSeq-count, R, DESeq2, GSEA
Check it out on PubMed Github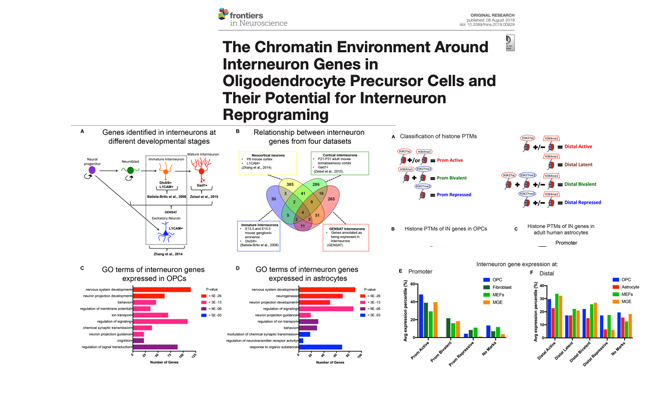
The chromatin environment around interneuron genes in NG2 cells and their direct reprogramming into GABAergic neuron-like cells.
Journal: Frontiers in Neuroscience 2019; 13: 829.
Our bioinformatic analysis of histone posttranslational modifications at interneuron genes in Oligodendrocyte precursor cells (OPCs) revealed that OPCs had significantly fewer bivalent and repressive histone marks at interneuron genes compared to astrocytes or fibroblasts.
Tools used: Python, Fastqc, Trimmomatic, HiSAT2, HTSeq-count, R, Bioconductor, DESeq2, GSEA, GOprofiler, MACS2, Bowtie2
Check it out on PubMed Github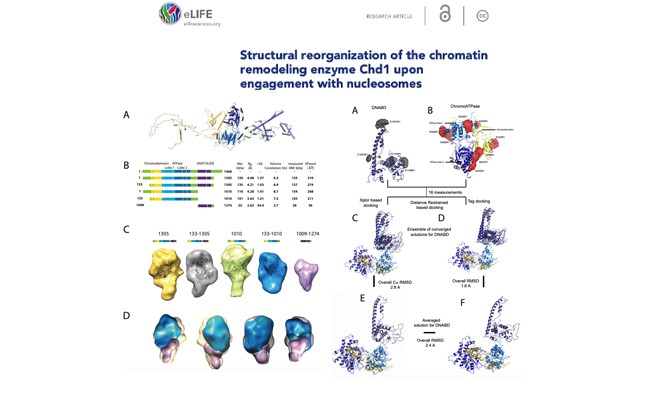
Structural reorganization of the chromatin remodeling enzyme Chd1 upon engagement with nucleosomes.
Journal: Elife. 2017 Mar 23;6.
We identified that the orientation of the DNA-binding domain, in Chd1, is mediated by sequences in the N-terminus and mutations to this part of the protein have positive and negative effects on Chd1 activity. These observations indicate that the unfavorable alignment of C-terminal DNA-binding region in solution contributes to an auto-inhibited state.
Tools used: Fastqc, Trimmomatic, Python, MACS2
Check it out on PubMed Github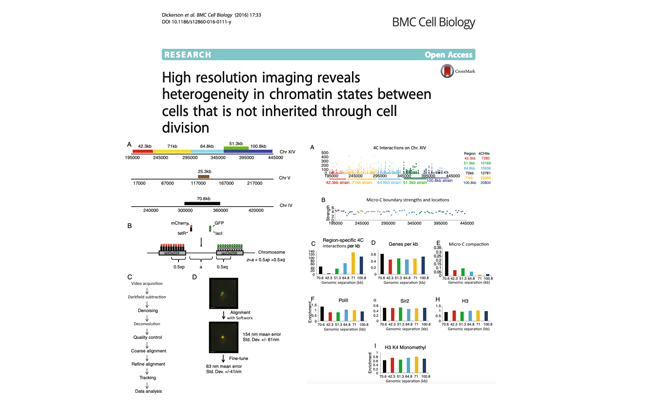
Histone degradation in response to DNA damage enhances chromatin dynamics and recombination rates.
Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2017 Feb;24(2):99-107.
Here we evaluated whether histones modification and eviction at sites of DNA breaks is localised to these sites or is spread genome wide. we propose that a generalized reduction in nucleosome occupancy is an integral part of the DNA damage response in yeast that provides mechanisms for enhanced chromatin mobility and homology search.
Tools used: Fastqc, Trimmomatic, Bowtie2, MACS2, Bedtools, Python
Check it out on PubMed Github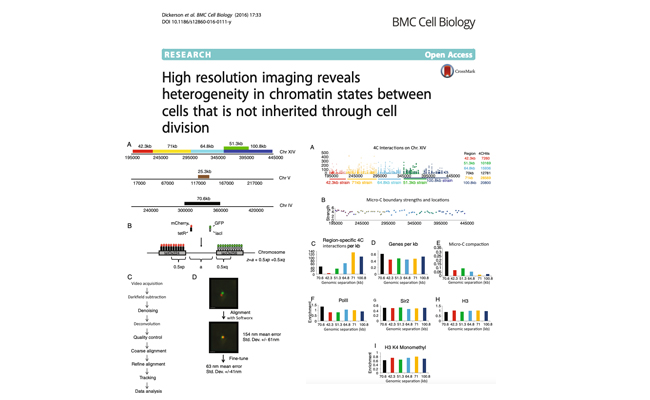
High resolution imaging reveals heterogeneity in chromatin states between cells that is not inherited through cell division.
Authors: Dickerson D, Gierliński M, Singh V, Kitamura E, Ball G, Tanaka TU, Owen-Hughes T.
Journal: BMC Cell Biol. 2016 Sep 8;17(1):33.
Genomes of eukaryotes exist as chromatin, and it is known that different chromatin states can influence gene regulation. Chromatin is not a static structure, but is known to be dynamic and vary between cells. In order to monitor the organisation of chromatin in live cells we have engineered fluorescent fusion proteins which recognize specific operator sequences to tag pairs of syntenic gene loci. The separation of these loci was then tracked in three dimensions over time using fluorescence microscopy.
Tools used: Fastqc, Trimmomatic, Bowtie2, Python, MACS2
Check it out on PubMed Github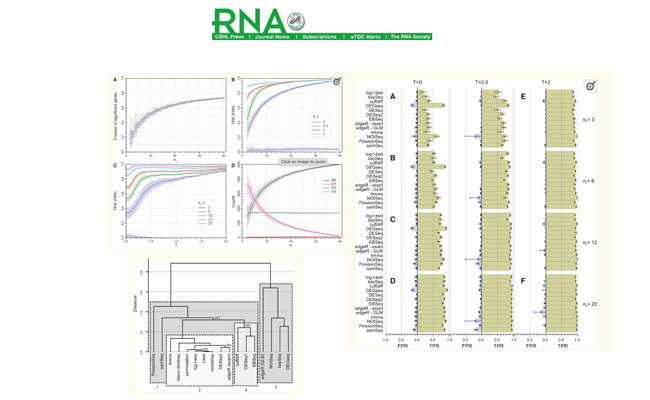
How many biological replicates are needed in an RNA-seq experiment and which differential expression tool should you use?
Journal: RNA. 2016 Jun;22(6):839-51.
An RNA-seq experiment with 48 biological replicates in each of two conditions was performed to answer these questions and provide guidelines for experimental design.
Tools used: Fastqc, Trimmomatic, STAR, FeatureCount, R, DESeq2, EdgeR, Limma, etc
Check it out on PubMed Github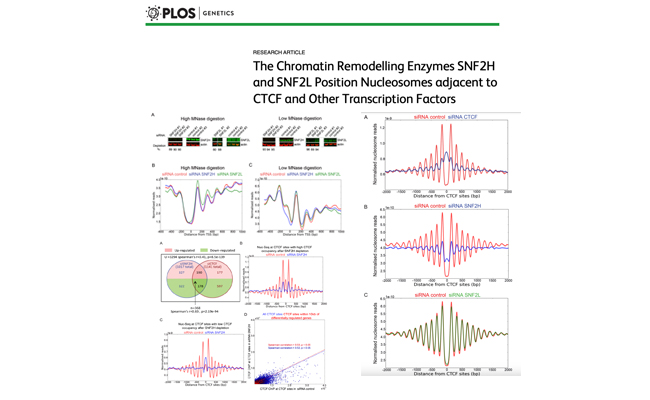
The Chromatin Remodelling Enzymes SNF2H and SNF2L Position Nucleosomes adjacent to CTCF and Other Transcription Factors.
Authors: Wiechens N, Singh V, Gkikopoulos T, Schofield P, Rocha S, Owen-Hughes T.
Journal: PLoS Genet. 2016 Mar 28;12(3).
Here we have sought to investigate which chromatin remodelling enzymes are responsible for this. We find that the ATP-dependent chromatin remodelling enzyme SNF2H plays a major role organising arrays of nucleosomes adjacent to the binding sites for the architectural transcription factor CTCF sites and acts to promote CTCF binding.
Tools used: Fastqc, Trimmomatic, HiSAT2, HTSeq-count, R, DESeq2, Python, MACS2, bedtools
Check it out on PubMed Github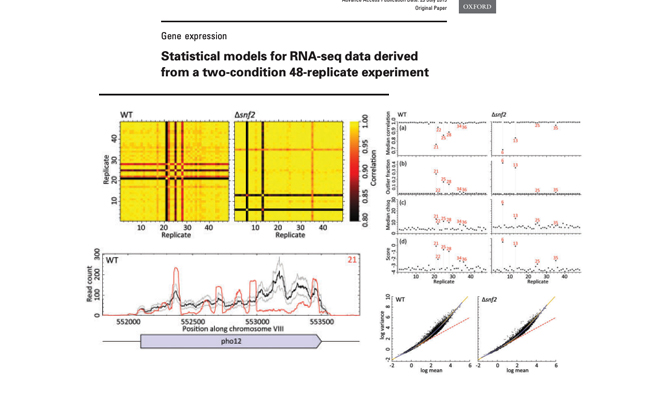
Article Statistical models for RNA-seq data derived from a two-condition 48-replicate experiment.
Journal: Bioinformatics. 2015 Nov 15;31(22):3625-30.
A 48-replicate RNA-seq experiment in yeast was performed and data tested against theoretical models. The observed gene read counts were consistent with both log-normal and negative binomial distributions, while the mean-variance relation followed the line of constant dispersion parameter of ∼0.01. The high-replicate data also allowed for strict quality control and screening of ‘bad’ replicates, which can drastically affect the gene read-count distribution.
Tools used: Fastqc, Trimmomatic, HiSAT2, HTSeq-count, R
Check it out on PubMed Github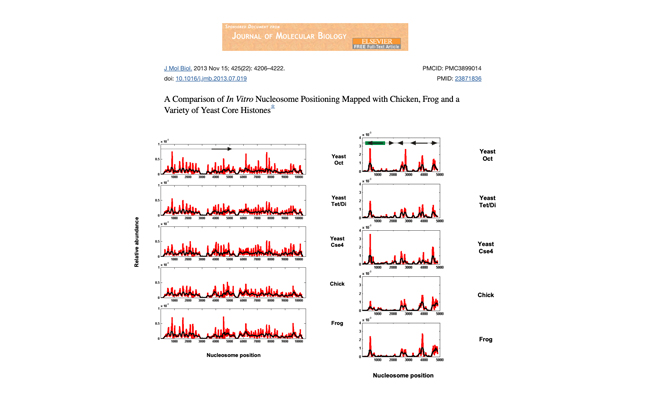
A comparison of in vitro nucleosome positioning mapped with chicken, frog and a variety of yeast core histones.
Authors: Allan J, Fraser RM, Owen-Hughes T, Docherty K, Singh V.
Journal: J Mol Biol. 2013 Nov 15;425(22):4206-22.
Using high-throughput sequencing, we have mapped sequence-directed nucleosome positioning in vitro on four plasmid DNAs containing DNA fragments derived from the genomes of sheep, drosophila, human and yeast.
Check it out on PubMed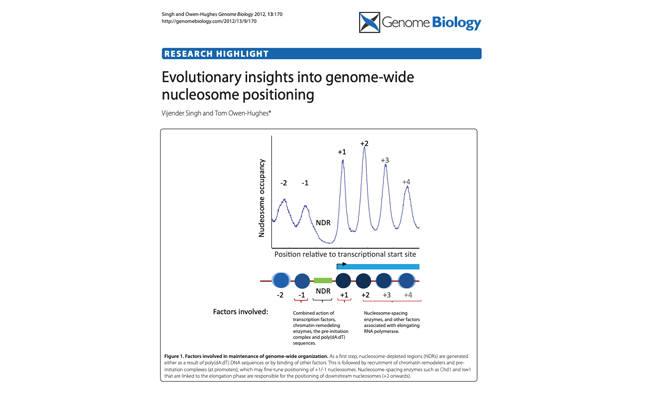
Evolutionary insights into genome-wide nucleosome positioning.
Authors: Singh V, Owen-Hughes T.
Journal: Genome Biol. 2012;13(9):170.
Review Article
Check it out on PubMed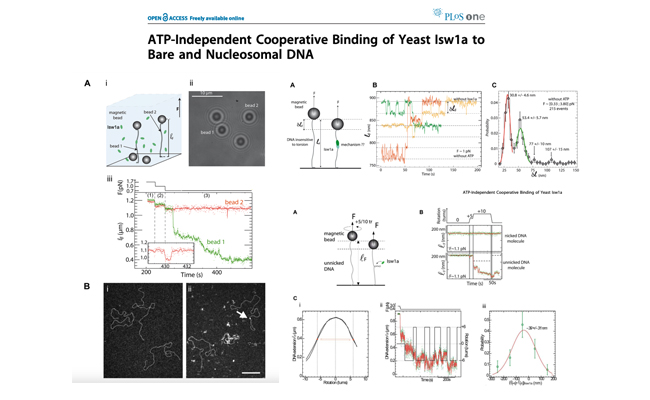
ATP-independent cooperative binding of yeast Isw1a to bare and nucleosomal DNA.
Journal: PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31845
Here we use TEM imaging and single molecule manipulation to investigate the interaction between DNA and yeast Isw1a. We show that Isw1a displays a highly cooperative ATP-independent binding to and bridging between DNA segments.
Check it out on PubMed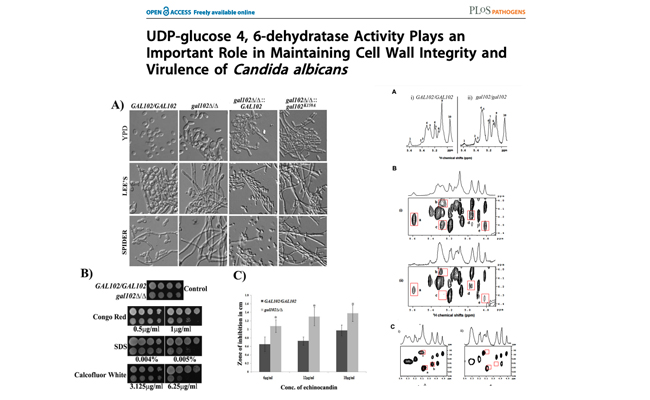
UDP-glucose 4, 6-dehydratase activity plays an important role in maintaining cell wall integrity and virulence of Candida albicans.
Journal: PLoS Pathog. 2011 Nov;7(11):
We report here that GAL102 in C. albicans encodes a homolog of dTDP-glucose 4,6-dehydratase, an enzyme that affects cell wall properties as well as virulence of many pathogenic bacteria. We found that GAL102 deletion leads to greater sensitivity to antifungal drugs and cell wall destabilizing agents like Calcofluor white and Congo red.
Check it out on PubMed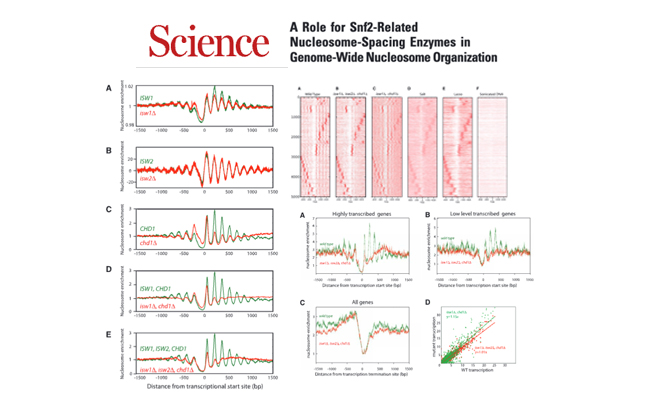
A role for Snf2-related nucleosome-spacing enzymes in genome-wide nucleosome organization.
Journal: Science. 2011 Sep 23;333(6050):1758-60.
Here, we show that the combined action of Isw1 and Chd1 nucleosome-spacing enzymes is required to maintain this organization. In the absence of these enzymes, regular positioning of the majority of nucleosomes is lost.
Tools used: Fastqc, Trimmomatic, Bowtie, Python
Check it out on PubMed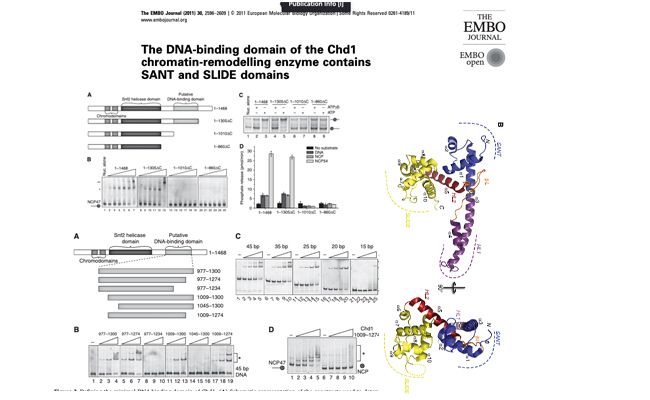
The DNA-binding domain of the Chd1 chromatin-remodelling enzyme contains SANT and SLIDE domains.
Authors: Ryan DP, Sundaramoorthy R, Martin D, Singh V, Owen-Hughes T.
Journal: EMBO J. 2011 May 27;30(13):2596-609.
Here, we show the DNA-binding domain is required for Saccharomyces cerevisiae Chd1 to bind and remodel nucleosomes. The crystal structure of this domain reveals the presence of structural homology to SANT and SLIDE domains previously identified in ISWI remodelling enzymes.
Check it out on PubMed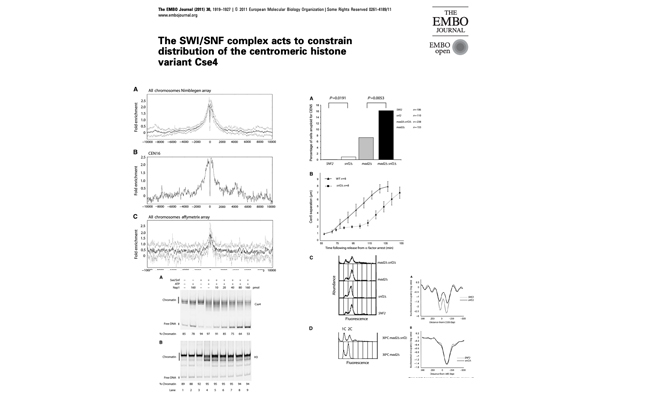
The SWI/SNF complex acts to constrain distribution of the centromeric histone variant Cse4.
Journal: EMBO J. 2011 May 18;30(10):1919-27.
We investigated the role of Swi/Snf in centromeric nucleosome maintainance in yeast.
Check it out on PubMed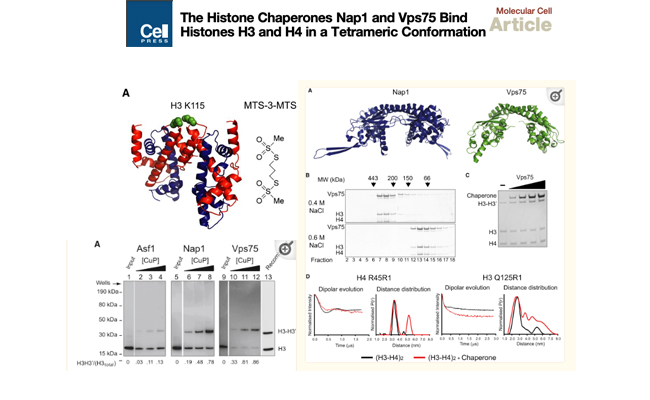
The histone chaperones Nap1 and Vps75 bind histones H3 and H4 in a tetrameric conformation.
Authors: Bowman A, Ward R, Wiechens N, Singh V, El-Mkami H, Norman DG, Owen-Hughes T.
Journal: Mol Cell. 2011 Feb 18;41(4):398-408.
Nucleosome assembly proteins (Nap proteins) represent a distinct class of histone chaperone. Using pulsed electron double resonance (PELDOR) measurements and protein crosslinking, we show that two members of this class, Nap1 and Vps75, bind histones in the tetrameric conformation also observed when they are sequestered within the nucleosome.
Check it out on PubMed
The key enzyme in galactose metabolism, UDP-galactose-4-epimerase, affects cell-wall integrity and morphology in Candida albicans even in the absence of galactose.
Authors: Singh V, Satheesh SV, Raghavendra ML, Sadhale PP.
Journal: Fungal Genet Biol. 2007 Jun;44(6):563-74.
We showed that S. cerevisiae GAL10 (ScGAL10), essential for survival in the presence of galactose, has not been reported to have defects in the absence of galactose, the C. albicans homolog shows these phenotypes during growth in the absence of galactose. Thus a functional CaGal10 is required not only for galactose metabolism but also for normal hyphal morphogenesis, colony morphology, maintenance of cell-wall integrity and for resistance to oxidative stress even in the absence of galactose.
Check it out on PubMed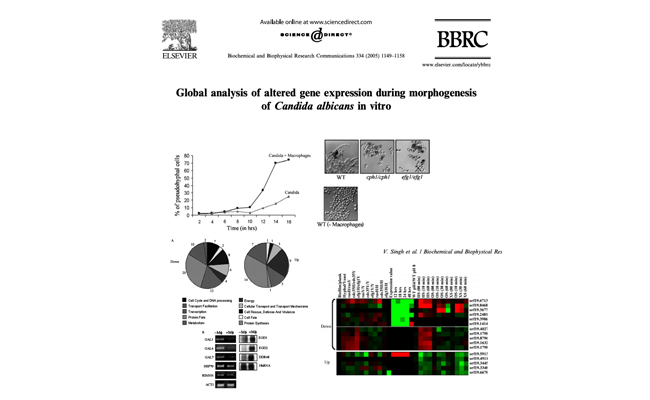
Global analysis of altered gene expression during morphogenesis of Candida albicans in vitro.
Authors: Singh V, Sinha I, Sadhale PP.
Journal: Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005 Sep 9;334(4):1149-58.
Based on the gene expression profiles and mutant studies we propose thatmorphogenetic response of C. albicans under the conditions used in these experiments is mainly through the pathways controlled by the above two regulators and not through the RIM101-dependent pathway.
Tools used: Microarray Analysis
Check it out on PubMed
Domainal organization of the lower eukaryotic homologs of the yeast RNA polymerase II core subunit Rpb7 reflects functional conservation.
Authors: Singh SR, Rekha N, Pillai B, Singh V, Naorem A, Sampath V, Srinivasan N, Sadhale PP.
Journal: Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Jan 2;32(1):201.
The subcomplex of Rpb4 and Rpb7 subunits of RNA pol II in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is known to be an important determinant of transcription under a variety of physiological stresses. In S.cerevisiae, RPB7 is essential for cell viability while rpb4 null strains are temperature sensitive at low and high temperatures. The rpb4 null strain also shows defect in sporulation and a predisposed state of pseudohyphal growth. We show here that, apart from S.cerevisiae Rpb7, the Rpb7 homologs from other lower eukaryotes like Schizosaccharomyces pombe, Candida albicans and Dictyostelium discoideum can complement for the absence of S.cerevisiae RPB7.
Check it out on PubMed